#
What is DevSecOps ?
TL;DR – DevSecOps integrates security from the first line of code through production operations, using collaboration and automation to make security everyone’s job and deliver software both fast and safe.
#
1. Why DevSecOps Matters
Traditional software delivery placed security checks at the end of the pipeline, often days or weeks before release. This “bolt‑on” approach can cause:
- Late‑stage vulnerabilities that are expensive to fix
- Friction between developers, ops, and security teams
- Release delays and dissatisfied customers
DevSecOps emerged to shift security left – embedding security practices, tooling, and mindset throughout the Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) lifecycle.
#
2. Working Definition
DevSecOps is the practice of integrating development (Dev), security (Sec), and operations (Ops) into a single, continuous workflow where every team member shares ownership of security through automated controls, rapid feedback, and collaborative culture.
Key attributes:
#
3. Pillars of DevSecOps
People & Culture
- Shared goals and KPIs
- Security champions embedded in squads
Process
- Security user stories & acceptance criteria
- Threat modeling and risk assessments in sprint planning
Technology
- Toolchain that integrates static (SAST), dynamic (DAST), dependency (SCA), and infrastructure (IaC) scanning
- Automated policy enforcement (e.g., OPA, Kyverno)
#
4. Security Activities Across the SDLC
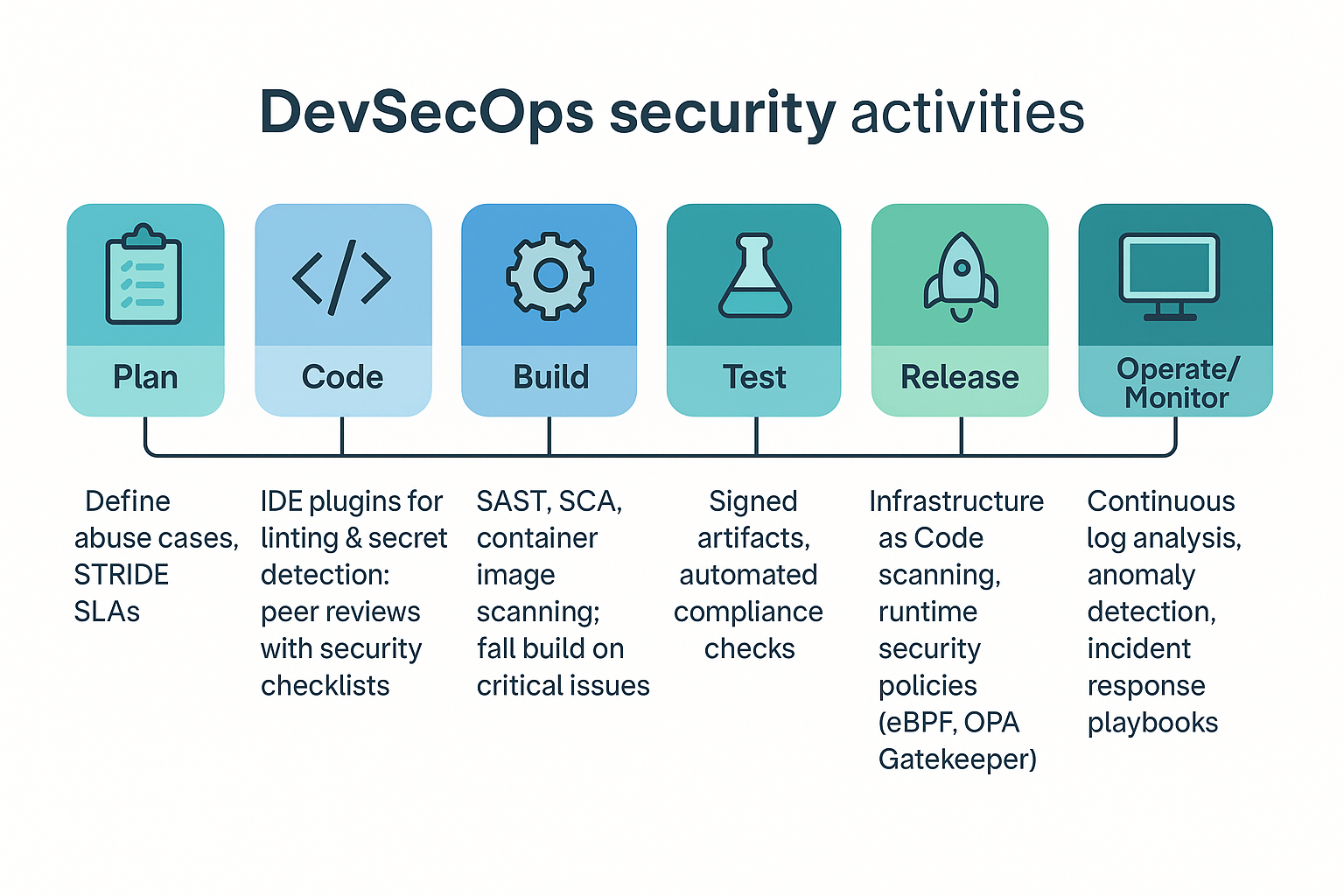
#
5. Benefits
- Faster release cycles – security gates become automated quality checks, not blockers
- Reduced mean‑time‑to‑remediate (MTTR) – vulnerabilities caught within minutes, not months
- Regulatory compliance – evidence is generated automatically (security as data)
- Improved team morale – developers gain confidence shipping secure code
#
6. Challenges & Pitfalls
- Cultural resistance – "Security slows us down" mindset
- Tool overload & false positives
- Skill gaps – developers unfamiliar with secure coding
- Legacy applications & infrastructure that are hard to automate
Mitigation tips: start small with one team, tune scanners aggressively, invest in training, and measure success.
#
7. Getting Started Checklist
- Identify a pilot project with an existing CI pipeline
- Integrate SAST & dependency scanning in pull requests
- Add infrastructure‑as‑code validation (e.g., tfsec, kube‑score)
- Define security SLAs (e.g., block on critical/high CVEs)
- Establish a feedback channel (chatops, dashboards)
- Run a "game day" to test incident response
- Iterate, expand, share lessons learned
#
8. Best Practices
- Security as Code – version‑control policies, baselines, and exceptions.
- Fail Fast, Fix Fast – stop the pipeline on critical issues, provide remediation snippets.
- Threat‑Driven Development – update threat models continuously.
- Security Champions – designate devs as first responders for security concerns.
- Metrics & KPIs – track time‑to‑fix, scan coverage, and defect density.
#
9. Conclusion
DevSecOps is not a toolset you can buy, but a cultural and technical shift where security becomes a continuous, automated, and collaborative part of delivering value. Teams that adopt DevSecOps release faster, lower risk, and build customer trust.
⚡️ Start small, automate ruthlessly, measure everything.
#
10. Further Reading
- Accelerate: The Science of Lean Software and DevOps — Forsgren, Humble & Kim
- The DevSecOps Playbook — Sounil Yu
- OWASP DevSecOps Guideline https://owasp.org/www-project-devsecops-guideline/
- DevOps Research & Assessment (DORA) Reports